Abstract
For the quick start of building opensearch, we can put the opensearch in the public network and control access by using basic authentication and domain access policy from the Fine-grain access controller. But this is a Critical alert from AWS security standards.
In this blog, I will walk through creating opensearch domain, putting it in VPC and how to use NGINX proxy to access OpenSearch Dashboards from outside a VPC that's using Amazon Cognito authentication
All AWS resources and settings are done by the Cloud development toolkit (CDK-typescript)
Table Of Contents
🚀 Create opensearch domain
The opensearch domain is created with VPC and security group which only allow private network access
For testing purpose, this code creates opensearch cluster with one node only, restricting 1 AZ with 1 subnet
const prefix = 'dev-opensearch'; const osVpc = new Vpc(this, `${prefix}-vpc`, { vpcName: prefix, natGateways: 1 }); const osSg = new SecurityGroup(this, `${prefix}-sg`, { securityGroupName: `${prefix}-sg`, vpc: osVpc }); const osDomain = new Domain(this, domainName, { domainName: domainName, version: EngineVersion.OPENSEARCH_1_2, removalPolicy: RemovalPolicy.DESTROY, enableVersionUpgrade: true, vpc: osVpc, vpcSubnets: [{ availabilityZones: [`${this.region}a`], onePerAz: true }], securityGroups: [osSg], capacity: { dataNodes: 1, dataNodeInstanceType: 't3.small.search', }, ebs: { volumeSize: 10, volumeType: EbsDeviceVolumeType.GENERAL_PURPOSE_SSD, },
🚀 Enable Amazon Cognito authentication
This step configures Amazon OpenSearch Service to use Amazon Cognito authentication for OpenSearch Dashboards
Using Amazon Cognito authentication requires cognito user pool and cognito identity pool.
Furthermore, we need to attach a role which gives Amazon OpenSearch Service permissions to configure the Amazon Cognito user and identity pools and use them for OpenSearch Dashboards/Kibana authentication. It is separate from the IAM role that allows users access to OpenSearch Dashboards/Kibana after they log in. A role with this name will be created in your account with the permissions defined in the role policy. If a role with this name already exists, it will be used to configure Cognito.
With that role, opensearch automatically creates user pool application for authentication
CDK code
opensearch role for consuming AWS cognito, it only needs the policy
AmazonOpenSearchServiceCognitoAccessconst cognitoOpensearchRole = new Role(this, 'dev-CognitoAccessForAmazonOpenSearch', { roleName: 'dev-CognitoAccessForAmazonOpenSearch', assumedBy: new ServicePrincipal('opensearchservice.amazonaws.com'), managedPolicies: [{managedPolicyArn: 'arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonOpenSearchServiceCognitoAccess'}] });Create user pool
const prefix = 'dev-opensearch'; const userpool = new UserPool(this, `${prefix}-userpool`, { userPoolName: `${prefix}-userpool`, signInAliases: { username: false, email: true }, standardAttributes: { email: { required: true } }, removalPolicy: RemovalPolicy.DESTROY, selfSignUpEnabled: true }); userpool.addDomain(`${prefix}-domain`, { cognitoDomain: { domainPrefix: 'devos' }, });Create identity pool, it's important to set
allowUnauthenticatedIdentities: trueconst identityPool = new IdentityPool(this, `${prefix}-identity-pool`, { identityPoolName: `${prefix}-identity`, allowUnauthenticatedIdentities: true });Enable Amazon Cognito authentication in opensearch, add the following code to the above opensearch domain stack
cognitoDashboardsAuth: { identityPoolId: identityPool.identityPoolId, userPoolId: userpool.userPoolId, role: cognitoOpensearchRole },
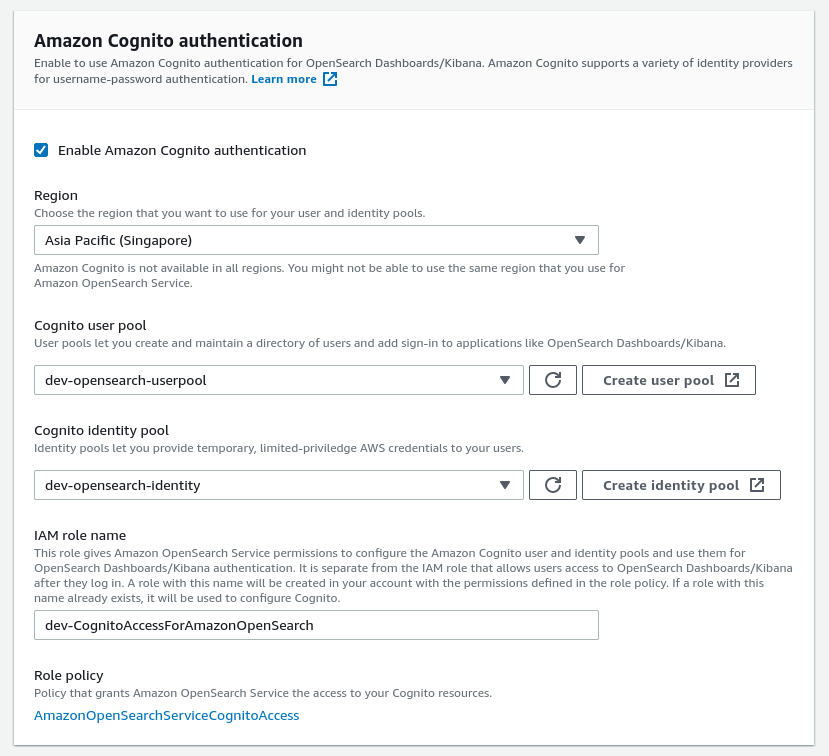
🚀 Fine-grained access control
The bigger picture: fine-grained access control and OpenSearch Service security
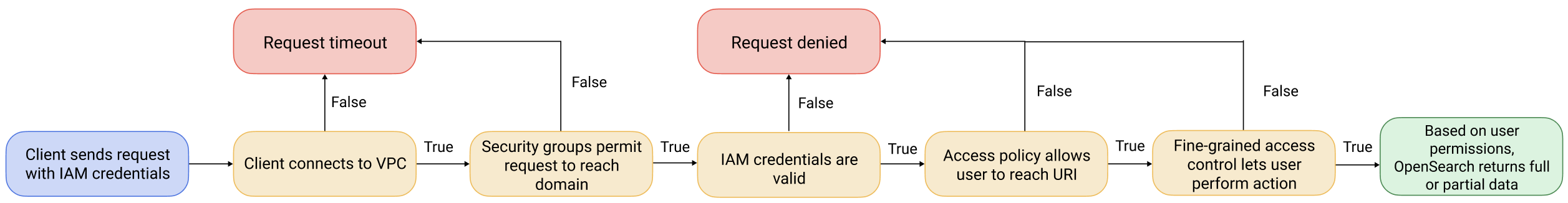
With VPC and Fine-grained access control enabled, we enable 3 layers of security for opensearch those are Network, Domain access policy and Fine-grained access control.
We're familiar with VPC that's why the main point of this blog is using nginx to access opensearch dashboard from outside of VPC
Domain access policy: After a request reaches a domain endpoint, the resource-based access policy allows or denies the request access to a given URI. In the following code, it separates 3 group users: default IAM role which is used by cognito identity pool, admin role (TBD) and anonymous user which only has some API request permission on a specific index. Following is the code snippet to create a domain access policy according to the 3 group users mentioned above.
accessPolicies: [ new PolicyStatement({ actions: ['es:ESHttpGet', 'es:ESHttpPost'], resources: [`arn:aws:es:${this.region}:${this.account}:domain/${domainName}/*`], principals: [new ArnPrincipal(identityPool.authenticatedRole.roleArn)], }), new PolicyStatement({ actions: ['es:*'], resources: [`arn:aws:es:${this.region}:${this.account}:domain/${domainName}/*`], principals: [new ArnPrincipal(adminAuthRole.roleArn)], }), /** * Support anonymous user * Some application/tool such as Kubernetes Event Exporter does not support IRSA but using basic authentication. * For using opensearch as a recevier, the tool just supports to use username/password * to communicate with opensearch domain, not support IRSA as aws-for-fluent-bit yet * Checkout: https://github.com/resmoio/kubernetes-event-exporter/issues/8 */ new PolicyStatement({ actions: [ "es:ESHttpDelete", "es:ESHttpPost", "es:ESHttpPut", "es:ESHttpPatch" ], resources: [`arn:aws:es:${this.region}:${this.account}:domain/${domainName}/kube-events*`], principals: [new AnyPrincipal()], }) ]Fine-grained access control: We enable and use this to add IAM role ARN and/or master user. After a resource-based access policy allows a request to reach a domain endpoint, fine-grained access control evaluates the user credentials and either authenticates the user or denies the request.
fineGrainedAccessControl: { masterUserArn: identityPool.authenticatedRole.roleArn },- From CDK stack lib, we can only add one IAM ARN but we can add more later manually as it says opensearch will not delete the old master user when adding a new one
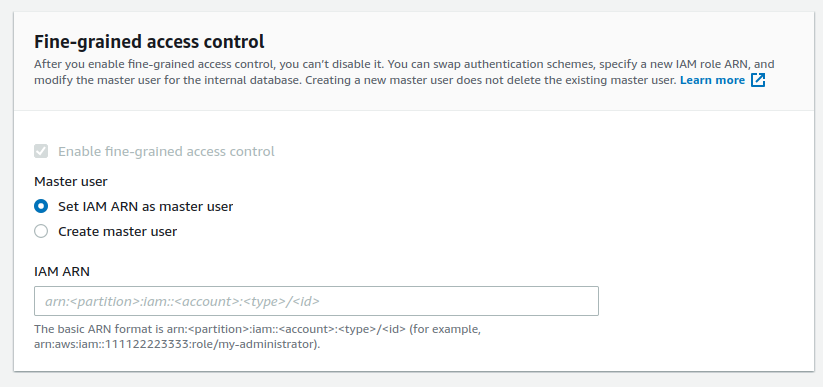
- We call the master user, but keep in mind that, the
domain access policydefines which actions the user can perform in opensearch
🚀 The overall architecture
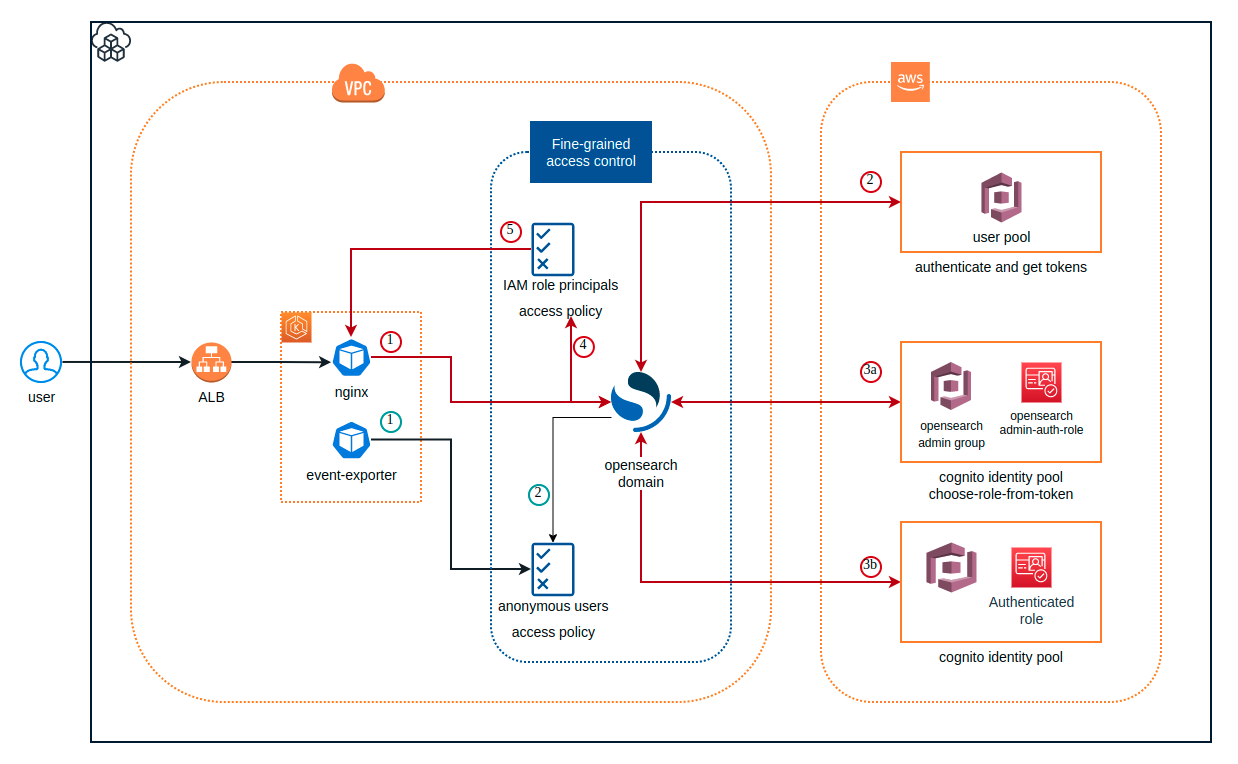
- There are two main flows you see here which is request from
nginxand request from thekube-event-exporter.
1. Nginx proxy to access opensearch dashboard
The nginx, here is k8s pod, which is in the same VPC network of the opensearch and allowed traffics based on the network interface of the Security group
After reaching opensearch domain, the request (not having access token yet) is redirected by opensearch to cognito user pool domain for signing. If signing successfully opensearch based on role-based access policy to handle the request. But which role is attached to the logined user?
In practice, we need to separate Developer user and admin user, that's why we see there're two cases for exchanging tokens from the architect
1.1 Developer user
If we just deploy the cdk code above, no more setup, the user eg.
developer@cloudopz.coassumes the default role from cognito identity pool
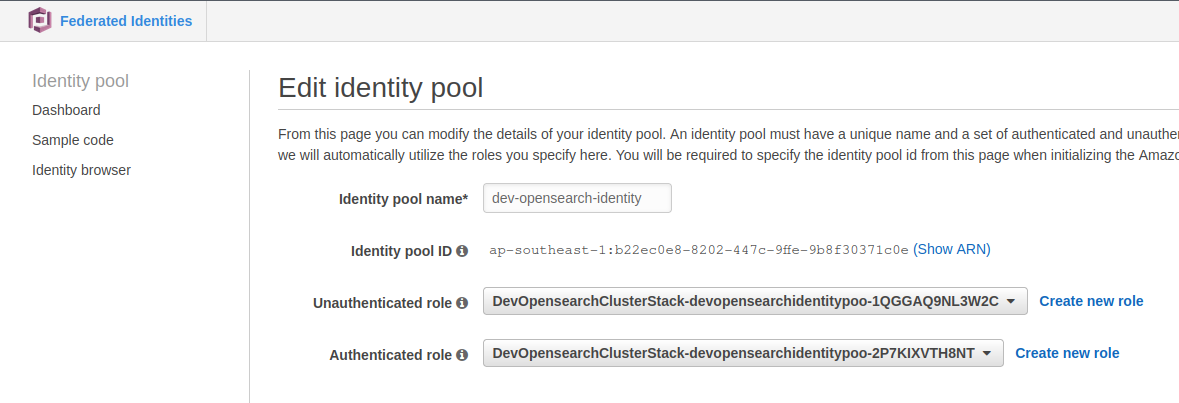
- Authenticated role: the role does not have any permission as it will assume the domain access policy
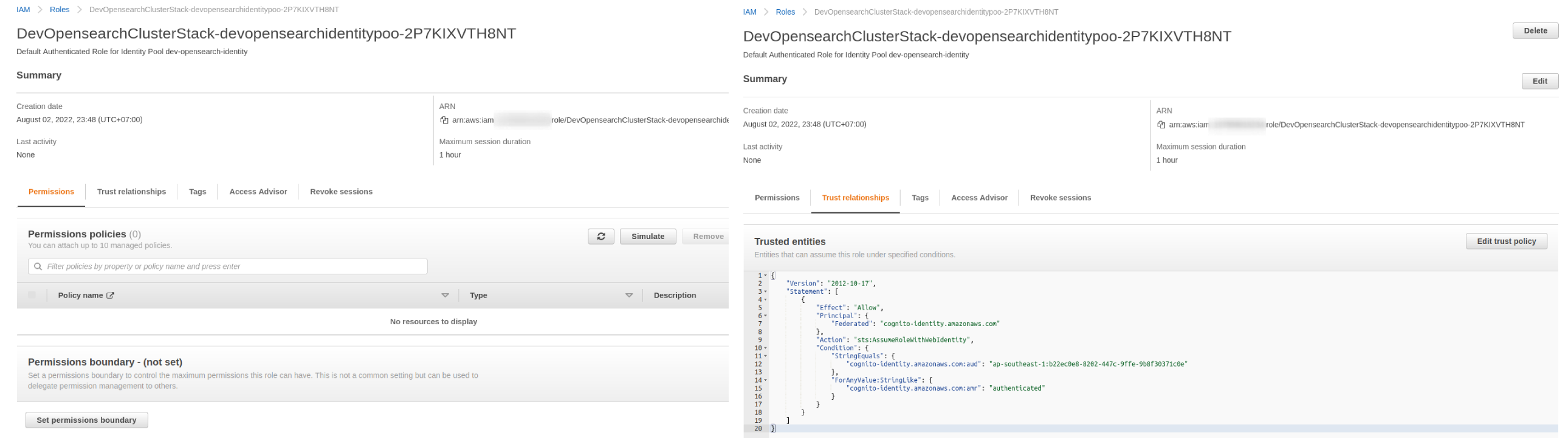
{ "Effect": "Allow", "Principal": { "AWS": "arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/DevOpensearchClusterStack-devopensearchidentitypoo-2P7KIXVTH8NT" }, "Action": [ "es:ESHttpGet", "es:ESHttpPost" ], "Resource": "arn:aws:es:ap-southeast-1:123456789012:domain/dev-opensearch/*" },
1.2. Admin role: In order to let a user from the user pool assume another role which is allowed more power permission, the following steps are required.
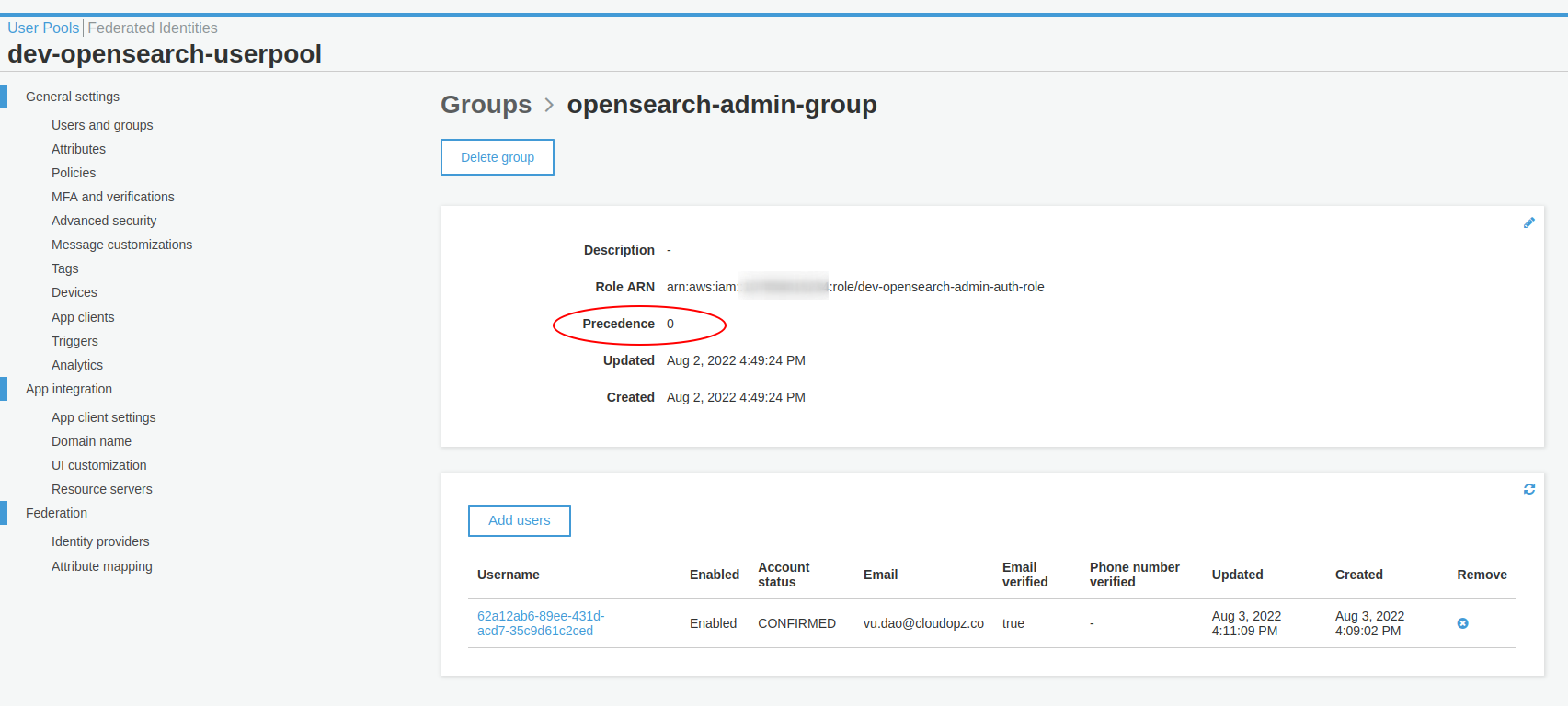
1.2.1. Add the user vu.dao@cloudopz.co to opensearch-admin-group group which is created by CDK and this group is associated with the role arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/dev-opensearch-admin-auth-role, remember to set the Precedence to 0 as the most priority of providing the token method
1.2.2. Update cognito identity pool to prioritize Choose role from token as the first option prior to the default one
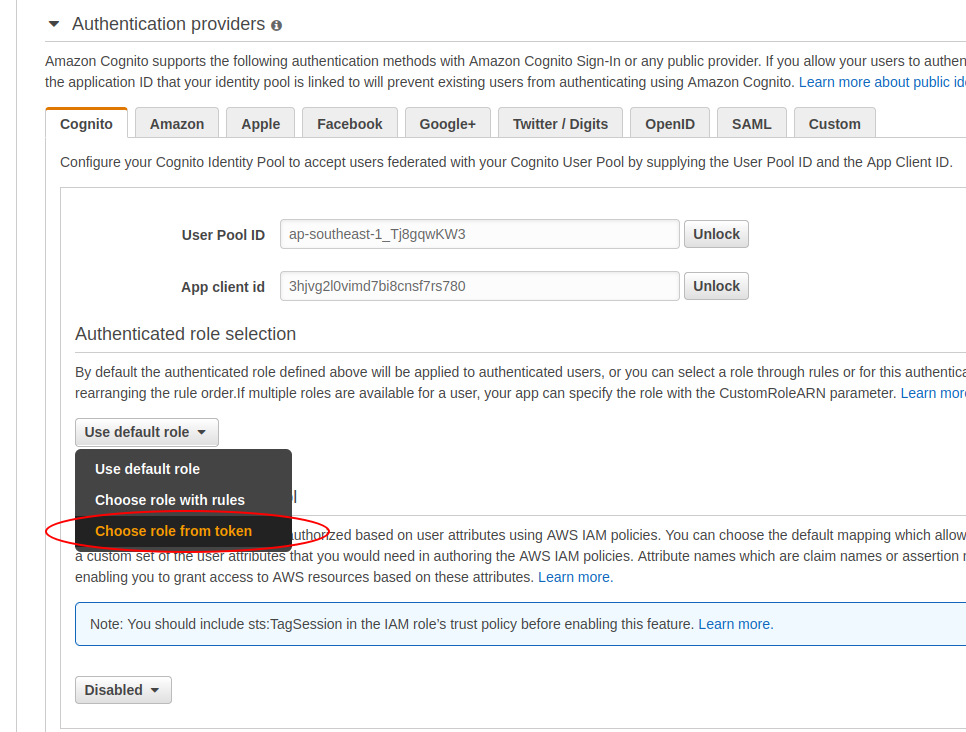
The user vu.dao@cloudopz.co will assume the role arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/dev-opensearch-admin-auth-role which has the following access policy
{ "Effect": "Allow", "Principal": { "AWS": "arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/dev-opensearch-admin-auth-role" }, "Action": "es:*", "Resource": "arn:aws:es:ap-southeast-1:123456789012:domain/dev-opensearch/*" }
All the AWS resources are on the right track, now let's have a look at nginx config (remember to replace
domain-endpointwith opensearch endpoint andcognito_hostwith Amazon Cognito domain)opensearch-nginx/ ├── conf.d │ └── default.conf ├── Dockerfile └── nginx.conf
2. Anonymous user
It's not a problem for using tools such as aws-for-fluent-bit which supports IRSA (IAM role for service account) and we just need to annotate a role to serviceAccount of
aws-for-fluent-bitand then add that role to opensearch using fine-grained access controlBut for other tools such as
kube-event-exporterwhich has not supported signing-service requests, so we can solve this by adding an anonymous user with limited resource for a specific index{ "Effect": "Allow", "Principal": { "AWS": "*" }, "Action": [ "es:ESHttpDelete", "es:ESHttpPost", "es:ESHttpPut", "es:ESHttpPatch" ], "Resource": "arn:aws:es:ap-southeast-1:123456789012:domain/dev-opensearch/kube-events*" }Let's check the result
🚀 Conclusion
Congratulations! TL;DR
In general, putting opensearch domain in VPC, enabling fine-grained access control and managing domain access policy is not much challenge. The thing is how we can access the domain outside of VPC and separate the developer and admin users by leveraging cognito user pool and identiy pool.
References:

