Table of contents
- Abstract
- Table Of Contents
- 🚀 Architecture Overview
- 🚀 Using CDK to create EFS and Access Point (AP)
- 🚀 Install EFS CSI Driver using helm-chart within airflow workers only
- 🚀 Create EFS storage class, PV, and PVC
- 🚀 Use CDK to create airflow IAM role
- 🚀 Use CDK to create Auto scaling groups (ASG)
- 🚀 Set up gitlab repo for git-sync sidecar
- 🚀 Create values.yaml
- 🚀 Airflow secrets
- 🚀 Deploy Airflow using helm chart
- 🚀 Create airflow ingress
- 🚀 Conclusion
Abstract
TL;DR
Airflow is one of the most popular tools for running workflows especially data-pipeline.
A successful pipeline moves data efficiently, minimizing pauses and blockages between tasks, and keeping every process along the way operational. Apache Airflow provides a single customizable environment for building and managing data pipelines
This post, it provides step-by-step to deploy airflow on EKS cluster using Helm for the default chart with customization in
values.yaml, cdk for creating AWS resources such as EFS, node group with Taints for pod toleration in the SPOT instance.
Table Of Contents
🚀 Architecture Overview
This blog guide you to deploy airflow on an existing EKS cluster using namespace
airflowand its resourcesPrerequisite:
EKS cluster
IAM admin role or enough permission to create AWS resources
CDK installation (Typescript)
Helm-chart
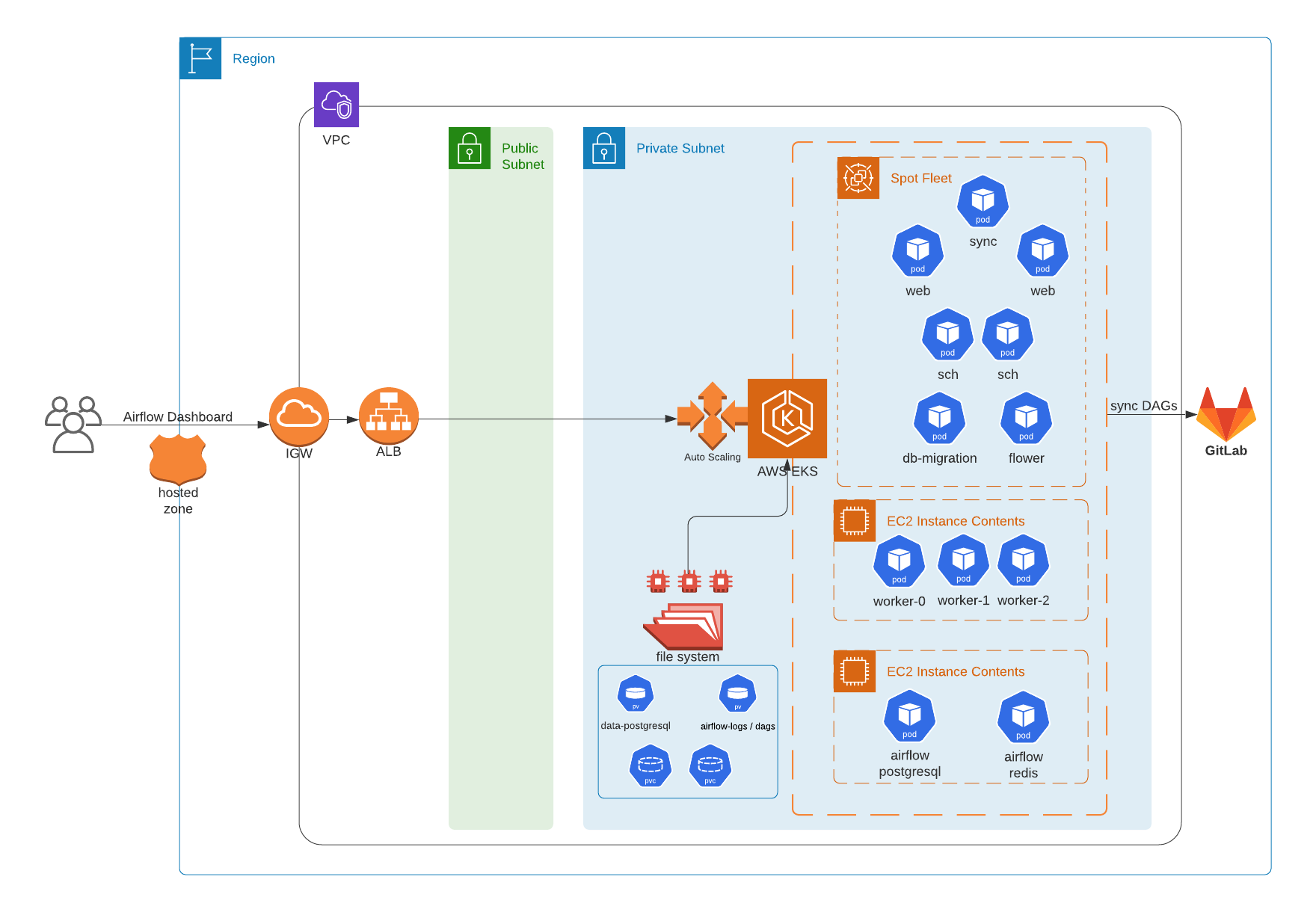
Airflow components: Worker, scheduler, web server, flower. Other things are airflow database, redis and sync.
Use EFS to share logs, DAGs between components such as worker, scheduler and webserver. Plus use EFS to store airflow database metadata
There are 3 node groups:
On-demand EC2: workers (If you can control the retries of Airflow task and DAGS, this group is better to use Spot instances instead)
On-demand EC2: Airflow database, pgBouncer and redis
Spot-fleet EC2: Schedulers, webs, and other components
🚀 Using CDK to create EFS and Access Point (AP)
It's necessary to create EFS as a way to persistent airflow DAGs, logs between workers and scheduler
Checkout AWS EKS With EFS CSI Driver And IRSA Using CDK to understand AWS EFS and CSI Driver provisioner
Create EFS within the
VPCof EKS cluster and addsecurity groupfor open access from EKS nodes
efs-stack.ts
import * as efs from '@aws-cdk/aws-efs';
import * as ec2 from '@aws-cdk/aws-ec2';
import { RemovalPolicy, App, Stack, StackProps, Tags } from '@aws-cdk/core';
export class AirflowEfsStack extends Stack {
constructor(scope: App, id: string, pattern: string, vpc: ec2.IVpc, ip: string, env_tag: string, props?: StackProps) {
super(scope, id, props);
const securityGroup = new ec2.SecurityGroup(this, 'AirflowEfsSG', {
vpc,
securityGroupName: `${pattern}-airflow-sg`,
description: 'Security group for EFS CSI',
allowAllOutbound: true
})
securityGroup.addIngressRule(ec2.Peer.ipv4(ip), ec2.Port.allTraffic(), 'Allow internal private vpc')
Tags.of(securityGroup).add('Name', `${pattern}-efs-sg`)
Tags.of(securityGroup).add('cdk:sg:stack', 'sg-stack')
Tags.of(securityGroup).add('env', env_tag)
const fileSystem = new efs.FileSystem(
this, 'AirflowEFS', {
vpc,
securityGroup,
fileSystemName: `${pattern}-airflow-efs`,
lifecyclePolicy: efs.LifecyclePolicy.AFTER_14_DAYS,
removalPolicy: RemovalPolicy.DESTROY
}
)
Tags.of(fileSystem).add('Name', `${pattern}-airflow-efs`)
Tags.of(fileSystem).add('cdk:efs:stack', `${pattern}-efs-${env_tag}`)
Tags.of(fileSystem).add('env', env_tag)
const fsAcccessPoint = fileSystem.addAccessPoint(
`${pattern}EFSAccesPoint`, {
posixUser: {
uid: '1001',
gid: '1001'
},
createAcl: {
ownerUid: '1001',
ownerGid: '1001',
permissions: '0700'
},
path: '/airflow/data'
}
)
Tags.of(fsAcccessPoint).add('Name', `${pattern}-data-airflow-pg`)
}
}

🚀 Install EFS CSI Driver using helm-chart within airflow workers only
- CSI driver provisioner is DaemonSet, it will deploy to all worker nodes as default but we can restrict to run EFS
kube-systempods for airflow nodes only by adding toleration and affinity invalues.yaml
values.yaml
controller:
tolerations:
- key: 'dedicated'
operator: 'Equal'
value: 'airflow'
effect: 'NoSchedule'
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: role
operator: In
values:
- airflow
node:
tolerations:
- key: 'dedicated'
operator: 'Equal'
value: 'airflow'
effect: 'NoSchedule'
nodeSelector:
role: airflow
- Deploy
helm repo add aws-efs-csi-driver <https://kubernetes-sigs.github.io/aws-efs-csi-driver/>
helm repo update
helm upgrade -i aws-efs-csi-driver aws-efs-csi-driver/aws-efs-csi-driver --values efs-values.yaml -n kube-system
🚀 Create EFS storage class, PV, and PVC
Pre-requisite: EFS and AP IDs which are created from the previous step
Update the EFS and AP ID to the storage class and persistent volume then create them
pvc.yaml
kind: StorageClass
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: af-efs-sc
provisioner: efs.csi.aws.com
parameters:
provisioningMode: efs-ap
fileSystemId: fs-3529be16
directoryPerms: "700"
gidRangeStart: "1000"
gidRangeEnd: "2000"
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: af-efs-pg-pv
spec:
capacity:
storage: 8Gi
volumeMode: Filesystem
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Retain
storageClassName: af-efs-sc
csi:
driver: efs.csi.aws.com
volumeHandle: fs-3529be15::fsap-0679931424ff5f0ce
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: data-airflow-postgresql
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
storageClassName: af-efs-sc
resources:
requests:
storage: 8Gi
- Get PVC, we will need this to update to
values.yamllater
$ kubectl get pvc
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE
data-airflow-postgresql Bound efs-pg-pv 8Gi RWX efs-sc 29h
🚀 Use CDK to create airflow IAM role
- The best practice is to use IAM role service account (IRSA), but within airflow we can create its role as an instance profile with permission for a node to join EKS cluster and permission to read/write EFS or other AWS resources
iamRole.ts
createWorkerRole(): IRole {
// Airflow IAM worker role
const worker_role = new Role(
this, 'AirflowIamRole', {
assumedBy: new ServicePrincipal('ec2.amazonaws.com'),
roleName: `${this.eksCluserName}-airflow`
}
);
const attachPolicies = ['AmazonEC2ContainerRegistryReadOnly', 'AmazonEKSWorkerNodePolicy', 'AmazonS3ReadOnlyAccess', 'AmazonEKS_CNI_Policy'];
for (var policy of attachPolicies) {
worker_role.addManagedPolicy(ManagedPolicy.fromAwsManagedPolicyName(policy))
}
Tags.of(worker_role).add('Name', `${this.eksCluserName}-airflow`)
Tags.of(worker_role).add('cdk:iam:stack', `${this.pattern}-iam-${this.env_tag}`)
Tags.of(worker_role).add('env', this.env_tag)
const autoscalingStatement = new PolicyStatement({
sid: 'AutoScalingGroup',
actions: [
"autoscaling:DescribeAutoScalingGroups",
"autoscaling:DescribeAutoScalingInstances",
"autoscaling:DescribeLaunchConfigurations",
"autoscaling:DescribeTags",
"autoscaling:CreateOrUpdateTags",
"autoscaling:UpdateAutoScalingGroup",
"autoscaling:TerminateInstanceInAutoScalingGroup",
"ec2:DescribeLaunchTemplateVersions",
"elasticfilesystem:*",
"tag:GetResources",
],
effect: Effect.ALLOW,
resources: ['*'],
conditions: {
'StringEquals': {"aws:RequestedRegion": this.region}
}
});
worker_role.addToPolicy(autoscalingStatement);
return worker_role;
};
Note: ASG launch template will add this Airflow role to
aws-authconfigmapmapRolesfor joining new nodes to the EKS clusterCheckout AWS EKS - Launch Template Of Node Group for understanding how IAM role in nodegroup works
🚀 Use CDK to create Auto scaling groups (ASG)
Why do we need auto scaling here? In order to handle workloads between when running workflows
Create a manage node group with spot instances for saving cost. Of course, we should care about spot instances that might be interrupted. If a workflow task gets interrupted due to node termination, you may lose a part of your progress, but the cost of losing ten minutes of progress is much lower than losing four hours of work.
Using Spot instances for long-running tasks can be disruptive if the node running the task gets terminated by Spot. Consider breaking long-running tasks into multiple sub-tasks with a shorter execution time that can be used to checkpoint a workflow’s progress.
We also recommend that you configure automatic retries in DAGs, especially when using Spot.
Two autoscaling groups: Instance types are based on the need of Airflow processes such as workload, data size, number of DAGs, tasks and their complexity
- ASG-pet: min 2, max 2
spot: 100%
type:
c5a.xlarge,c5a.largecomponents: 2
sch, 2web, 1flower, 1sync
- ASG-sts (stateful set): min 1, max 3
calculate the number of workers and auto-scaling
spot: 100%
type:
c5a.2xlarge,c5a.largecomponents: workers
- ASG-db (database): min 1, max 1
on-demand: 100%
type:
c5a.xlargecomponents: airflow database, redis, pgBouncer
asg-stack.ts
import { Stack, App, Tags, StackProps} from '@aws-cdk/core';
import { Cluster, Nodegroup, CapacityType, TaintEffect } from '@aws-cdk/aws-eks'
import { Role, ServicePrincipal, ManagedPolicy, PolicyStatement, Effect, IRole } from '@aws-cdk/aws-iam';
import * as ec2 from '@aws-cdk/aws-ec2';
interface Ec2Type {
pet: Array<string>,
pet_size: Array<number>,
sts: string,
sts_size: Array<number>,
db: string
};
export class AirflowAsgStack extends Stack {
public eks_cluster: any;
public worker_role: any;
public airflowSG: any;
public eksCluserName: string;
public launchTemplate: any;
constructor(public scope: App, id: string, public pattern: string, public vpc: ec2.IVpc, public vpcSg: ec2.ISecurityGroup,
public region: string, public ip: string, ec2_types: Ec2Type, public env_tag: string, props?: StackProps) {
super(scope, id, props);
this.eksCluserName = 'us-eks'
// EKS cluster
this.eks_cluster = Cluster.fromClusterAttributes(
this, `EksCluster${pattern.toUpperCase()}`, {
vpc,
clusterName: this.eksCluserName
}
);
this.launchTemplate = this.createLaunchTemplate();
// Airflow-SG to workers
this.airflowSG = this.createAirflowSG();
this.worker_role = this.createWorkerRole();
this.createAsgPet(ec2_types.pet, ec2_types.pet_size);
this.createAsgSts(ec2_types.sts, ec2_types.sts_size);
this.createAsgDb(ec2_types.db);
};
createAirflowSG(): any {
/**
* Airflow security group
*/
const airflowSG = new ec2.SecurityGroup(this, 'AirflowairflowSG', {
vpc: this.vpc,
securityGroupName: 'airflow-priv-sg',
description: 'Security group to access to worker in private vpc',
allowAllOutbound: true
});
airflowSG.connections.allowFrom(airflowSG, ec2.Port.allTcp(), 'Allow node to communicate with each other');
airflowSG.connections.allowFrom(this.vpcSg, ec2.Port.allTcp(), 'Allow nodes in another ASG communicate to airflow nodes');
Tags.of(airflowSG).add('Name', 'airflow-priv-ssh-sg');
Tags.of(airflowSG).add('cdk:sg:stack', `${this.pattern}-sg-${this.env_tag}`);
Tags.of(airflowSG).add('env', this.env_tag);
return airflowSG;
};
createLaunchTemplate(): any {
/**
* More about launch-templates: https://github.com/awsdocs/amazon-eks-user-guide/blob/master/doc_source/launch-templates.md
* Notes:
* - Nodegroup auto-generates role if not specify
* - Launch template node group automatically add the worker role to aws-auth configmap
*/
const airflowLaunchTemplate = new ec2.LaunchTemplate(this, 'AirflowLaunchTemplate-lt', {
launchTemplateName: 'airflow-asg-lt',
securityGroup: this.airflowSG,
blockDevices: [{
deviceName: '/dev/xvda',
volume: ec2.BlockDeviceVolume.ebs(20)
}],
keyName: `${this.pattern}-airflow`
});
Tags.of(airflowLaunchTemplate).add('Name', 'airflow-asg-lt');
Tags.of(airflowLaunchTemplate).add('cdk:lt:stack', `${this.pattern}:lt:${this.env_tag}`);
Tags.of(airflowLaunchTemplate).add('env', this.env_tag);
return airflowLaunchTemplate;
}
createAsgPet(types: Array<string>, sizes: Array<number>) {
/**
* ASG Pet is used to assign deployments. Due to using spot instances so recommendation min size 2
*/
const asgNodeGroupName = 'eks-airflow-nodegroup-pet';
const asgPet = new Nodegroup(this, 'AirflowPetAsg', {
nodegroupName: 'eks-airflow-nodegroup-pet',
subnets: this.eks_cluster.vpc.selectSubnets({subnetType: ec2.SubnetType.PRIVATE}),
cluster: this.eks_cluster,
capacityType: CapacityType.SPOT,
nodeRole: this.worker_role,
instanceTypes: [
new ec2.InstanceType(types[0]),
new ec2.InstanceType(types[1])
],
minSize: sizes[0],
maxSize: sizes[1],
labels: {
'role': 'airflow',
'type': 'af-stateless',
'lifecycle': 'spot'
},
taints: [
{
effect: TaintEffect.NO_SCHEDULE,
key: 'dedicated',
value: 'airflow'
}
],
tags: {
'Name': 'eks-airflow-nodegroup-pet',
'cdk:asg:stack': `${this.pattern}-asg-${this.env_tag}`
},
launchTemplateSpec: {
id: this.launchTemplate.launchTemplateId!
}
});
};
createAsgSts(type: string, sizes: Array<number>) {
/**
* ASG STS: Assign Airflow workers
*/
const asgNodeGroupName = 'eks-airflow-nodegroup-sts';
const asgStatefulSet = new Nodegroup(this, 'AirflowStsAsg', {
nodegroupName: asgNodeGroupName,
subnets: this.eks_cluster.vpc.selectSubnets({subnetType: ec2.SubnetType.PRIVATE}),
cluster: this.eks_cluster,
nodeRole: this.worker_role,
instanceTypes: [new ec2.InstanceType(type)],
capacityType: CapacityType.SPOT,
minSize: sizes[0],
maxSize: sizes[1],
labels: {
'role': 'airflow',
'type': 'af-stateful',
'lifecycle': 'spot'
},
taints: [
{
effect: TaintEffect.NO_SCHEDULE,
key: 'dedicated',
value: 'airflow'
}
],
tags: {
'Name': 'eks-airflow-nodegroup-sts',
'cdk:asg:stack': `${this.pattern}-asg-${this.env_tag}`
},
launchTemplateSpec: {
id: this.launchTemplate.launchTemplateId!
}
});
};
createAsgDb(type: string) {
/**
* ASG Db: Assign Airflow database and redis to this worker group
*/
const asgNodeGroupName = 'eks-airflow-nodegroup-db';
const asgStatefulSet = new Nodegroup(this, 'AirflowDbAsg', {
nodegroupName: asgNodeGroupName,
subnets: this.eks_cluster.vpc.selectSubnets({subnetType: ec2.SubnetType.PRIVATE}),
cluster: this.eks_cluster,
nodeRole: this.worker_role,
instanceTypes: [new ec2.InstanceType(type)],
capacityType: CapacityType.ON_DEMAND,
minSize: 1,
maxSize: 1,
labels: {
'role': 'airflow',
'type': 'af-db',
'lifecycle': 'on-demand'
},
taints: [
{
effect: TaintEffect.NO_SCHEDULE,
key: 'dedicated',
value: 'airflow'
}
],
tags: {
'Name': 'eks-airflow-nodegroup-db',
'cdk:asg:stack': `${this.pattern}-asg-${this.env_tag}`
},
launchTemplateSpec: {
id: this.launchTemplate.launchTemplateId!
}
});
};
}
- Deploy
$ cdk deploy AirflowAsgStackUS
- Check result
# kf get node |grep 20-eks
ip-172-10-13-169.us-east-1.compute.internal Ready <none> 2d2h v1.18.20-eks-c9f1ce
ip-172-10-41-179.us-east-1.compute.internal Ready <none> 2d14h v1.18.20-eks-c9f1ce
ip-172-10-51-199.us-east-1.compute.internal Ready <none> 23h v1.18.20-eks-c9f1ce
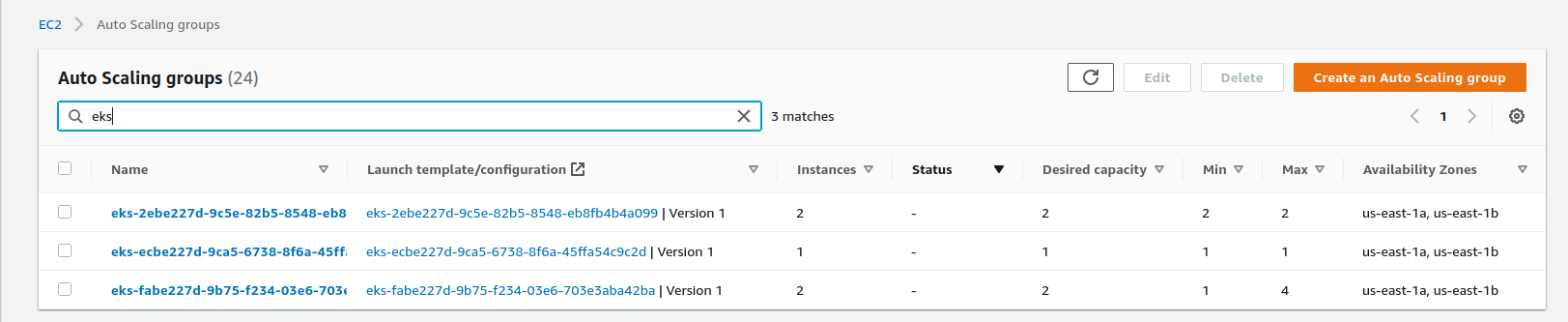
- IMPORTANT: The above code contains creating Airflow security group, you should check out Understand Pods communication for a deep understanding of how EKS node join EKS cluster and how Pods communicate
🚀 Set up gitlab repo for git-sync sidecar
- Create a new project to store DAGs on Git and let git-sync update DAGs automatically.

- Create user
airflowand add to project as reporter/developer

- Generate its token as impersonating which will be used later

🚀 Create values.yaml
values.yaml is used to customize some attributes from airflow helm chart to adapt with our system and deployments such as credentials, Airflow configs, Pods assignment, autoscaling, etc.
Use community airflow helm chart (not the official one). Template
values.yamlfrom airflow-helm/chartsCustomizations 1. Update airflow image if you'd like to deploy from your own one or use the latest public one
airflow: image: repository: apache/airflow tag: 2.1.4-python3.9 pullPolicy: IfNotPresent2. Persist airflow logs using EFS
logsairflow: kubernetesPodTemplate: securityContext: fsGroup: 65534 sync: securityContext: fsGroup: 65534 scheduler: securityContext: fsGroup: 65534 web: securityContext: fsGroup: 65534 workers: securityContext: fsGroup: 65534 flower: securityContext: fsGroup: 65534 logs: ## the airflow logs folder ## path: /opt/airflow/efs/logs persistence: enabled: true subPath: "" storageClass: "efs-sc" accessMode: ReadWriteMany size: 1Gi
Reference How to persist airflow logs? for more options.
3. Update web.service.type to NodePort for later use Ingress
web:
service:
type: NodePort
4. Set up workers replicas for a balance workload How to set up celery worker autoscaling?
5. Add toleration to airflow components - Airflow nodes will only accept airflow Pods - Global setting airflow.defaultTolerations
defaultTolerations:
- key: 'dedicated'
operator: 'Equal'
value: 'airflow'
effect: 'NoSchedule'
- For other extra components such as
postgresql,redis,pgBouncerwe need to addtolerationsat each field
6. Add nodeAffinity to assign airflow components to their node group
- For deployment services such as web, scheduler, sync, flower
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: type
operator: In
values:
- af-stateless
- For stateful service such as workers
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: type
operator: In
values:
- af-stateful
- For postgresql, redis, pgBouncer
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: type
operator: In
values:
- af-db
7. Persist DAGs using git-sync 7.1 git-sync sidecar (SSH auth) - Pre-requiste: Create Linux user airflow, generate its rsa ssh-key, add public key to airflow gitlab user and then use id_rsa to generate secret
$ kubectl create secret generic \
airflow-ssh-git-secret \
--from-file=id_rsa=$(pwd)/id_rsa \
--namespace airflow
secret/airflow-ssh-git-secret created
- Get gitlab
known_hosts
ssh-keyscan -H gitlab.cloudopz.co >> known_hosts
- Update
values.yamlatdags.gitSync
dags:
## the airflow dags folder
##
path: /opt/airflow/efs/dags
gitSync:
enabled: true
repo: "git@gitlab.cloudopz.co:devops/airflow-dags.git"
branch: "master"
revision: "HEAD"
syncWait: 60
sshSecret: "airflow-ssh-git-secret"
sshSecretKey: "id_rsa"
# "known_hosts" verification can be disabled by setting to ""
sshKnownHosts: |-
gitlab.cloudopz.co ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAABAQDD18bjpsGTussTrWvrU9LzqDdb0DJ5XVlOvmv4E+svIN6ItUvS3UrNNKiABs9IlexsEnDTdYTfZkV14Ft7f79lTeLKqvEJowF6RZg1SDOtW4ljPxRUh8n8MgGftI37m3baRYBqdsSbTebjfDRkykgI3k5AW+Lw9syeckncL3ZLAUQ894bh/uIqu4tCP59UlxZ43B6n6nna9g+ZFz/EGCsQTxPsTUIy13Lrgeh6kLQk77zvxdz838/JDH7ELdmd1nwCJIXOKhFwwSDkRUAkHgVSHWsFZdfNM4Na3TRBR0IUCnEqwDuEqSlTh1yfv1oymu6FeA/JaiTgfhvDVleB4wSx
7.2 git-sync sidecar (HTTP auth)
- Create a secret with gitlab token key get from "Set up gitlab repo for git-sync sidecar"
kubectl create secret generic \
airflow-http-git-secret \
--from-literal=username=airflow \
--from-literal=password=EKZvPi8TCKVaNSz45rjn \
--namespace airflow
- Update
values.yamlatdags.gitSync
dags:
## the airflow dags folder
##
path: /opt/airflow/efs/dags
gitSync:
enabled: true
repo: "https://gitlab.cloudopz.co/devops/airflow-dags.git"
branch: "master"
revision: "HEAD"
syncWait: 60
httpSecret: "airflow-http-git-secret"
httpSecretUsernameKey: username
httpSecretPasswordKey: password
8. Database - PostgreSQL Chart with enabling debug and using EFS
We already created the PVC from Create EFS Access Point for postgresql volume
Update
values.yaml(Note: DEBUG enabled is optional)
postgresql:
enabled: true
postgresqlDatabase: airflow
postgresqlUsername: postgres
postgresqlPassword: airflow
existingSecretKey: "postgresql-password"
extraEnv:
- name: BITNAMI_DEBUG
value: "true"
persistence:
enabled: true
storageClass: "efs-sc"
existingClaim: "data-airflow-postgresql"
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
size: 8Gi
master:
podAnnotations:
cluster-autoscaler.kubernetes.io/safe-to-evict: "true"
volumePermissions:
enabled: true
9. Create Airflow variables
We can use plain/text or Secrets/Configmaps
10. Generate Fernet
Airflow uses Fernet to encrypt passwords in the connection configuration and the variable configuration. It guarantees that a password encrypted using it cannot be manipulated or read without the key. Fernet is an implementation of symmetric (also known as “secret key”) authenticated cryptography.
Generating Fernet key
from cryptography.fernet import Fernet
fernet_key= Fernet.generate_key()
print(fernet_key.decode()) # your fernet_key, keep it in secured place!
🚀 Airflow secrets
For airflow users, reference Access Control to assign proper permissions.
airflow-secret.yamlapiVersion: v1 kind: Secret metadata: name: airflow-secret namespace: airflow data: airflow-admin-password: == airflow-user-password: airflow-viewer-password: = airflow-fernet: = clh-password: == db_user: db_password: ttdb_user: = ttdb_password: == slack_host: slack_webhook: == # airflow database postgresql-password: = # git-sync access token airflow-gitlab-user: == airflow-gitlab-token: =
🚀 Deploy Airflow using helm chart
- The community usage helm chart
# add this repo as "airflow-stable"
helm repo add airflow-stable https://airflow-helm.github.io/charts
helm repo update
kubectl create namespace airflow
helm upgrade -i "airflow" airflow-stable/airflow \
--version "8.5.2" \
--namespace "airflow" \
--values values.yaml
- Check PVC
$ kubectl get pvc
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE
airflow-logs Bound pvc-177df93c-331f-4514-9733-9e67be7612ee 1Gi RWX af-efs-sc 7d18h
data-airflow-postgresql Bound af-efs-pg-pv 8Gi RWX af-efs-sc 8d

- Check pods
$ kubectl get pod -owide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
airflow-db-migrations-8666f9b775-p9n6p 2/2 Running 0 7d2h 10.0.7.85 ip-10-0-7-188.ec2.internal <none> <none>
airflow-flower-79bf6f7b95-mst9x 2/2 Running 0 6d15h 10.0.6.117 ip-10-0-6-175.ec2.internal <none> <none>
airflow-pgbouncer-75b9ddcf89-q8vkf 1/1 Running 0 7d2h 10.0.9.109 ip-10-0-9-82.ec2.internal <none> <none>
airflow-postgresql-0 1/1 Running 0 7d2h 10.0.9.65 ip-10-0-9-82.ec2.internal <none> <none>
airflow-redis-master-0 1/1 Running 0 7d2h 10.0.9.237 ip-10-0-9-82.ec2.internal <none> <none>
airflow-scheduler-6dc74f564f-44tzx 2/2 Running 0 6d15h 10.0.6.33 ip-10-0-6-175.ec2.internal <none> <none>
airflow-scheduler-6dc74f564f-cb5d4 2/2 Running 0 7d2h 10.0.15.232 ip-10-0-15-181.ec2.internal <none> <none>
airflow-sync-connections-8579c86d44-dg9jq 2/2 Running 0 6d15h 10.0.15.150 ip-10-0-15-181.ec2.internal <none> <none>
airflow-sync-pools-7f4f55776b-qdcjn 2/2 Running 0 6d15h 10.0.6.203 ip-10-0-6-175.ec2.internal <none> <none>
airflow-sync-users-6d98bb49ff-zx5rs 2/2 Running 0 6d15h 10.0.15.140 ip-10-0-15-181.ec2.internal <none> <none>
airflow-sync-variables-7f9959cd-j8p8x 2/2 Running 0 6d15h 10.0.6.27 ip-10-0-6-175.ec2.internal <none> <none>
airflow-web-7f46664c6c-bvgls 2/2 Running 0 7d2h 10.0.15.111 ip-10-0-15-181.ec2.internal <none> <none>
airflow-web-7f46664c6c-vq6kr 2/2 Running 0 6d15h 10.0.6.4 ip-10-0-6-175.ec2.internal <none> <none>
airflow-worker-0 2/2 Running 0 7d2h 10.0.7.100 ip-10-0-7-188.ec2.internal <none> <none>
airflow-worker-1 2/2 Running 0 7d2h 10.0.14.153 ip-10-0-14-28.ec2.internal <none> <none>
- We see that the two workers locate on different nodes. Check node to be taints and pods are in toleration
$ kubectl describe node ip-10-0-7-188.ec2.internal | grep Taints -B 1
CreationTimestamp: Thu, 15 Jul 2021 07:19:29 +0000
Taints: dedicated=airflow:NoSchedule
kubectl describe pod airflow-worker-0 |grep Tolerations
Tolerations: dedicated=airflow:NoSchedule
$ kubectl describe pod airflow-worker-1 |grep Tolerations
Tolerations: dedicated=airflow:NoSchedule
- Check git-sync for up-to-date DAGs. The DAG file
101_postgres_operator.py

$ kubectl exec -it airflow-worker-0 -- ls -la efs/dags/repo/
Defaulting container name to airflow-worker.
Use 'kubectl describe pod/airflow-worker-0 -n airflow' to see all of the containers in this pod.
total 8
drwxr-sr-x 2 65533 nogroup 67 Jul 15 16:33 .
drwxrwsrwx 4 root nogroup 82 Jul 15 16:33 ..
-rw-r--r-- 1 65533 nogroup 71 Jul 15 16:33 .git
-rw-r--r-- 1 65533 nogroup 3221 Jul 15 16:33 101_postgres_operator.py
-rw-r--r-- 1 65533 nogroup 0 Jul 15 16:33 README.md
🚀 Create airflow ingress
airflowingress.k8s.yaml
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-protocol: HTTP
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/certificate-arn: arn:aws:acm:ap-northeast-2:123456789012:certificate/b8299bf5-ae3b-4f69-zzzz-xxxxyyyy
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/group.name: dev
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/group.order: "9"
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/listen-ports: '[{"HTTPS":443}]'
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: alb
labels:
dev: airflow
name: airflow
namespace: airflow
spec:
rules:
- host: airflow.vinceredev.com
http:
paths:
- backend:
serviceName: airflow-web
servicePort: 8080

🚀 Conclusion
With all of the steps above, you can now deploy airflow in EKS cluster with control assignment of airflow components to AWS node group
By using Amazon EC2 Spot, you can reduce your spending on EC2 instances significantly with minimal configuration changes.
By using EFS with CSI driver you can persist data, and logs cross multiple zones.
By using CDK, you get more familiar to create IaC and Kubernetes yaml as code.


