Table of contents
- Abstract
- Table Of Contents
- 🚀 Solution overview
- How does it work?
- 🚀 Network Firewall Rule Group
- 🚀 Dynamodb table
- 🚀 EventBridge
- 🚀 Step functions
- 🚀 Lambda functions
- We walked through all resources which are going to deploy in this solution, and see the flow in more detail
- 🚀 Using Pulumi to create infrastructure as code
- 🚀 Conclusion
Abstract
Rather than spending time manually reacting to security alerts or looking at the GuardDuty/ Security hub dashboard, you can instead focus on activities such as enhancing application protection layers and improving your security program.
This blog is a combination of AWS services such as guard duty, security hub, event bridge, step functions, network firewall rule group, lambda function and slack notification to provide the automation.
And we use Pulumi to deploy those services as code.
Table Of Contents
🚀 Solution overview
Amazon GuardDuty is a continuous security monitoring service that analyzes and processes data from VPC flow logs, cloudTrail, S3 data events, etc. Based on this data, GuardDuty analysis and detection by using threat intelligence feeds, signatures, anomaly detection, and machine learning in the AWS Cloud.
The automation provided in this blog post is focused on blocking traffic to and from suspicious remote hosts. GuardDuty detection of unintended communication with remote hosts triggers a series of steps, including blocking of network traffic to those hosts by using a Network Firewall, and notification of security operators.
All in serverless by using eventBridge with event pattern from
aws.securityhubsource. For pattern matches such as HIGH or CRITICAL severity findings, as well as suspicious IP addresses, the event rule triggers step functions for remediation.AWS Step Functions is a serverless orchestration service that lets you combine AWS Lambda functions and other AWS services to build business-critical applications. Step Functions service also provides retry and error-handling logic, while Lambda functions to interact with networking controls to block traffic, and with a database to store data about blocked remote IP addresses.

How does it work?
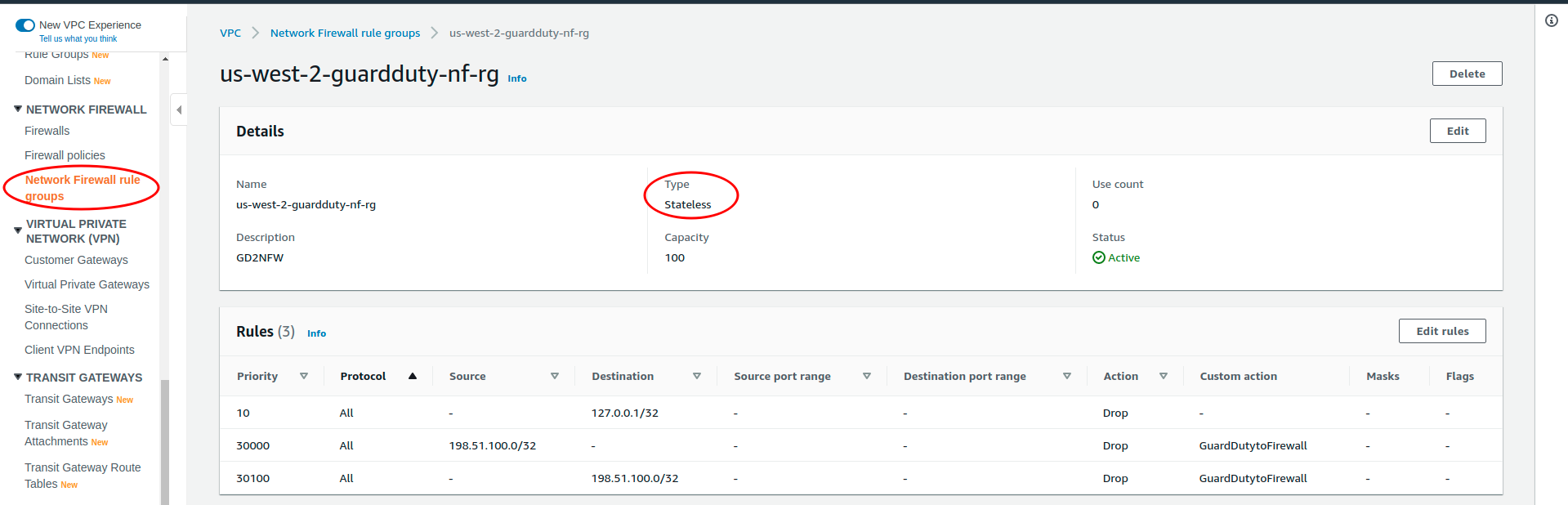
🚀 Network Firewall Rule Group
- This rulegroup is used to block traffic to and from suspicious remote hosts using
STATELESStype and actiondrop
🚀 Dynamodb table
The DDB tables are used to store the blocked IPs with attributes
HostIp,CreatedAtBilling Mode:
PAY_PER_REQUEST

🚀 EventBridge
Define rules with flowing patterns where the
sourceis fromaws.securityhubcatch-ipv4:
{ "detail": { "findings": { "ProductFields": { "aws/guardduty/service/action/networkConnectionAction/remoteIpDetails/ipAddressV4": [{ "exists": true }] } } }, "detail-type": ["Security Hub Findings - Imported"], "region": ["us-west-2"], "source": ["aws.securityhub"] }Other findings:
{ "detail": { "findings": { "Severity": { "Label": ["HIGH", "CRITICAL"] } } }, "detail-type": ["Security Hub Findings - Imported"], "region": ["us-west-2"], "source": ["aws.securityhub"] }
🚀 Step functions
sechub-record-ip: include three lambda functionsadd_ip_func,update_rule_group_func,send_finding_func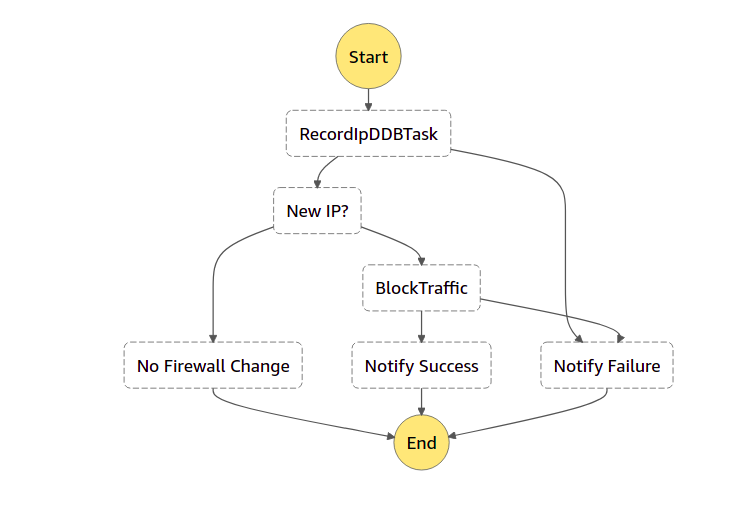
sechub-send-findings: which uses lambda function resource
send_finding_func
sechub-prune-ip: lambda functions
get_ip_func,remove_ip_func,send_finding_func,update_rule_group_func
🚀 Lambda functions
add-ip-to-ddb: The function parses the event to get
HostIpand then adds it to Dynamodb (DDB) table, if it's actually new IP then return a record which includes the IP list and flagNewIP=True, otherwise, flagNewIP=Falsedue to IP already existing in DDBget-ip-from-ddb: This function is called by the scheduled state machine to get all blocked IPs in DDB which are expired (blocking time > 720 hours)
remove-ip-from-ddb: Based on the input of expired IPs from previous step functions, remove those IPs from DDB and then return the rest of the IPs
update-nf-rg: This function overrides current Network firewall rule group with the input combined with current
send-gd-finding: This function sends a notification of success or failure for any blocking IPs or high/critical findings.
We walked through all resources which are going to deploy in this solution, and see the flow in more detail

🚀 Using Pulumi to create infrastructure as code
Source code in
TypeScript: aws-guardduty-sechub GitHub repository. The following commands show how to deploy the solution using PulumiFirst, need to set Pulumi configs such as AWS region, AWS account, AWS profile and webhook URL of slack channel
pulumi config set aws:region us-west-2 pulumi config set aws:profile myprofile pulumi config set --secret aws-guardduty-sechub:webhook_url https://slack.channel.com/<ID>Preview the stack
pulumi previewDeploy stack
pulumi upCheck the result on the Pulumi graph view

🚀 Conclusion
In this blog post, we walked through a solution to use AWS services, including Amazon EventBridge, AWS step function, AWS Lambda, and Amazon DynamoDB, to correlate AWS Security Hub findings from multiple different AWS security services.
By automating blocking traffic from suspicious IP addresses and sending high and critical findings to slack, we can prioritize and improve our security response.
References:

